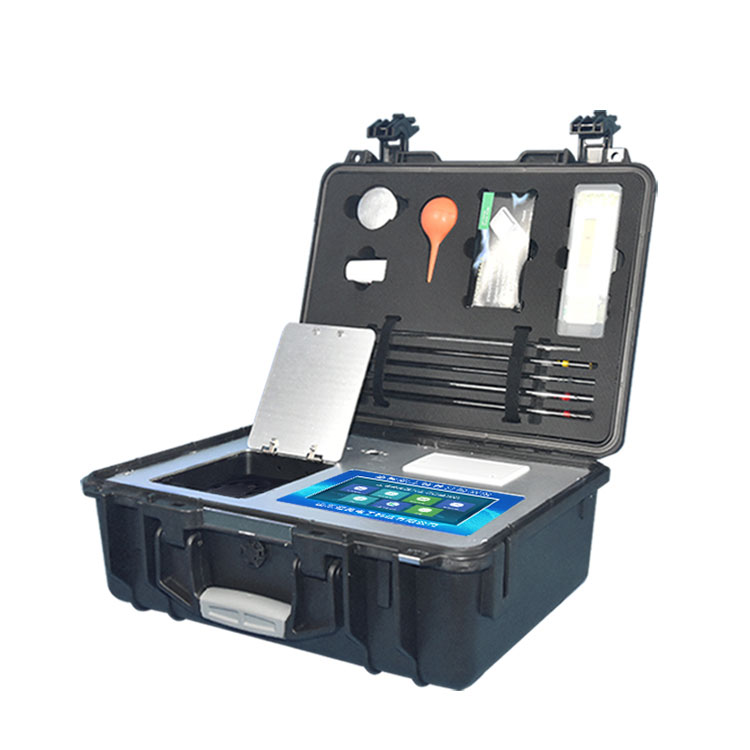
Sensors of the Soil Moisture Monitor are placed in soil at different depths, enabling accurate detection of soil physical properties. For example, soil moisture sensors utilize the principle of frequency domain reflectometry: they emit electromagnetic waves of a specific frequency and determine the volume percentage of soil moisture based on the correlation between soil dielectric constant and water content. Temperature sensors can obtain soil temperature in real-time, and they can also be equipped with conductivity sensors, pH sensors, etc., to comprehensively understand soil fertility, chemical properties, and other conditions.
The data collector receives electrical signals from the sensors, converts them into digital signals, and stores them. With the help of IoT technology, the digital signals are transmitted to remote servers or user terminal devices through wireless communication modules such as GPRS or LoRa. Users can view soil moisture data via mobile apps, computer web pages, etc. Cloud platforms or software analyze the collected historical data to explore the changing patterns and trends of soil moisture.
Soil moisture monitors are used for irrigation and drought resistance. On one hand, they provide a basis for precise irrigation. In the past, farmers mostly relied on experience for irrigation, which often led to insufficient or excessive irrigation. With soil moisture monitors, farmers can determine the actual water content based on real-time soil moisture data, and combine it with the water needs of crops at different growth stages to determine the irrigation time and amount. For instance, during the jointing stage of wheat, if the monitoring station detects that the soil water content is below the appropriate range, farmers can irrigate in a timely manner and control the water volume according to the data, which not only meets the growth needs but also avoids waste of water resources.
On the other hand, soil moisture monitors can realize drought warning. By analyzing historical and real-time data, the system can predict the changing trend of soil moisture. When it is predicted that soil moisture will continue to decrease, which may lead to drought, it will send warning information to users. Farmers can make early preparations for irrigation, rationally allocate water resources, and reduce the damage of drought to crops.

This paper addresses:https://www.fengtusz.com/industry/797.html