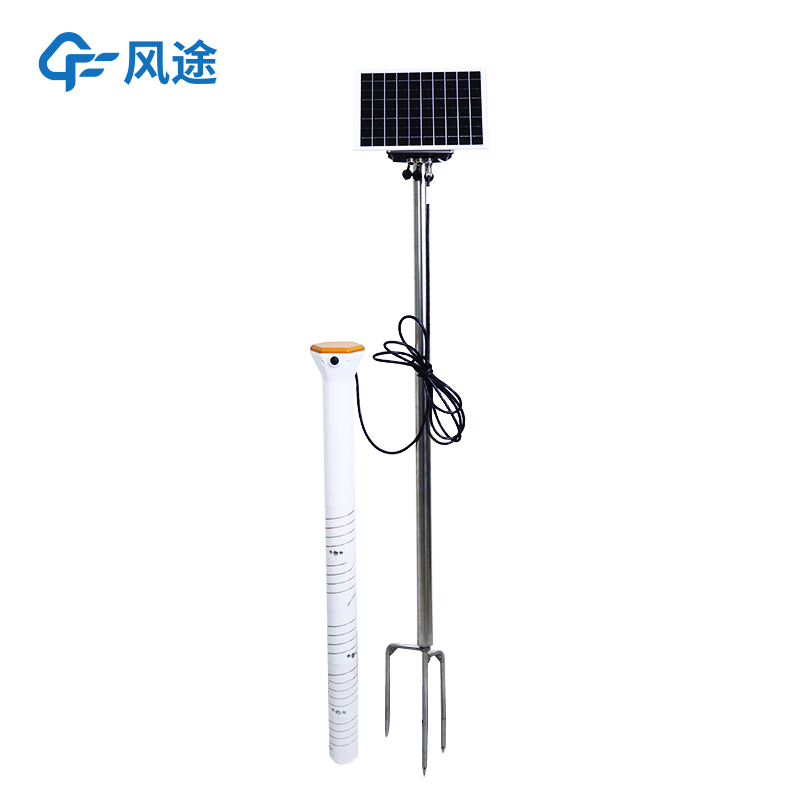
A soil moisture monitoring station comprises multiple components: sensors, data collectors, transmission modules, and power supply systems. Sensors serve as the core components, with common types including Frequency Domain Reflectometry (FDR) and Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) sensors. These sensors can penetrate different soil layers to precisely measure key indicators such as soil volumetric water content and relative water content. Additionally, auxiliary sensors for soil temperature and electrical conductivity are equipped to provide a comprehensive understanding of soil conditions. The data collector is responsible for gathering data from sensors, performing analog-to-digital conversion, storage, and preliminary processing. The transmission module uses wireless communication technologies like 4G and LoRa to real-time transmit collected data to agricultural management platforms or user terminals, enabling users to access soil moisture information anytime, anywhere. The power supply system employs solar panels to convert solar energy into electrical energy during daylight, powering system components and charging the battery; at night or during rainy days, the battery supplies power to ensure continuous operation.
Key Role in Precision Irrigation
Precision irrigation is a critical approach to agricultural water conservation, and the soil moisture monitoring station provides the key basis for this practice. By real-time monitoring of soil moisture content, farmers can accurately grasp changes in soil moisture status and formulate scientific irrigation plans based on the actual water requirements of crops at different growth stages, avoiding over-irrigation or insufficient irrigation. For example, in vegetable cultivation, water demands vary across growth stages. With data from the monitoring station, irrigation volume and timing can be precisely adjusted to meet vegetable growth needs while improving water resource utilization efficiency. In arid regions, the station can promptly detect soil water shortages and remind farmers to irrigate in a timely manner, ensuring normal crop growth; in areas with relatively abundant water resources, precision irrigation can reduce water waste.
Extended Significance for Agricultural Water Conservation
Beyond supporting precision irrigation, the soil moisture monitoring station holds multiple important implications for agricultural water conservation. On one hand, long-term monitoring and analysis of soil moisture data help farmers understand soil water retention capacity and moisture variation patterns, enabling them to adopt corresponding soil improvement measures to enhance water retention. On the other hand, the station can integrate with intelligent irrigation systems to achieve automated irrigation control, reducing labor costs and energy consumption.

This paper addresses:https://www.fengtusz.com/industry/775.html